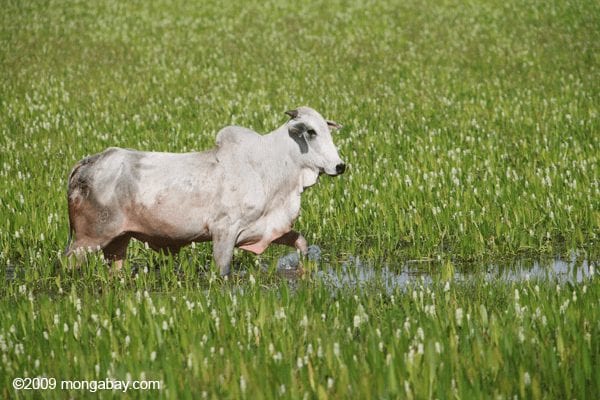

Taxing underutilized land in the Amazon could conserve forests, boost productivity, and alleviate poverty, argues study.
Cracking down on tax evasion and taxing unused land would help slow deforestation for land speculation in the Brazilian Amazon, argues a new report published by Imazon.
The report, O potencial do Imposto Territorial Rural contra o desmatamento especulativo na Amazônia, uses satellite imagery and publicly available data on properties and tax payment rates in the Amazon state of Pará. It finds that tax evasion in the state is widespread, topping 270 million reais ($108 million) a year, mostly from landowners declaring below market values for their holdings and overstating the extent of their properties to get around limitations on how much forest they can legally clear.
The result is both high deforestation — some 600,000 ha of forest were cleared in the area annually between 2010 and 2013 — and underutilization of cleared land. Neither provide much in the way of benefit to Brazil.
Study authors Daniel Silva da Silva and Paulo Barreto suggest that updating rules governing “productive use” of land would help rectify the situation by undercutting incentives for land speculation. Currently the bar for “productive use” of land for cattle ranching — overwhelmingly the biggest use of deforested land in the Brazilian Amazon — is set at 0.15 to 0.5 head of cattle per hectare. At that level, speculators can clear forest and add a few cattle in hopes of eventually selling the land to more intensive ranchers or for industrial soy farms.
Raising the cut-off for tax breaks to two head per hectare would encourage more productive use of pasture, while cutting an important subsidy for speculation. The study argues that efficient ranchers wouldn’t be much affected by the change, since they are already producing at higher levels. Additionally, curbing speculation would free up more land for productive activities, which the authors claim would help reduce poverty.
Cattle ranching is easily the largest direct driver of deforestation in Brazil, accounting for more than 60 percent of cleared land in the region. However as noted by the study, a significant proportion of clearing for pasture is actually a vehicle to speculate on rising land price: cleared land in the Amazon fetches significantly higher prices than forested lands.
Source: Mongabay
This post was published on 5 de November de 2014
States with the most deforestation in January were Mato Grosso, Roraima and Pará Deforestation…
According to the Green Radar report, in 2024, out of the 146 companies assessed, 6…
A survey of more than 3,500 lawsuits showed an increase in punishments, while payment of…
A group made up of specialists from 23 different professions trained in the Sustainable Amazon…
The degraded area increased due to burning, especially in August and September In 2024,…
The program is scheduled to last 15 years and will include local indigenous peoples and…